IN OTHER LANGUAGES

The bacteriostatic effect of PhytoAqua and a competing product on Vibrio parahaemolyticus was determined by spread plate method and test tube method respectively, and the bacteriostatic effect of PhytoAqua and a competitor product on Escherichia coli was measured by spread plate method, and it was found that for both Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Escherichia coli, PhytoAqua showed a stronger inhibitory ability than the competitor product.
Escherichia coli (ATCC: 25922), Vibrio parahaemolyticus (ATCC:17802), PhytoAqua, a competing product, brain-heart extract broth, Vibrio parahaemolyticus medium, sodium chloride, MH medium, anhydrous ethanol, purified water
Autoclave, constant temperature incubator.
Sample extraction: the competing product was extracted by ultrasonic extraction with 50% ethanol for 30 minutes, and the final concentration of the extract was 100g/L. PhytoAqua was diluted to 100g/L with pure water.
Preparation of bacterial suspension: take Escherichia coli, add 100ml of sterilized brain-heart leachate broth, activate at 37°C constant temperature incubator for 24 hours, aspirate 1ml of activated bacterial suspension in 100ml of brain-heart leachate broth, and expand the cultivation at 37°C constant temperature incubator for 24 hours, determine the concentration of the final bacterial suspension by plate counting method, and dilute it to 1*105cfu/ml in sterile water for spare; take Vibrio parahaemolyticus, add 100ml of 3% NaCl brain-heart leachate broth, activate and expand the cultivation at 37°C constant temperature incubator for 24 hours.
Spread plate method to measure the inhibitory effect on E. coli: MH medium was autoclaved, cooled to about 80°C and the product was added according to a certain ratio, and the product and the medium were mixed well so that the final concentration of the product was 0.1g/L, 0.2g/L, 0.5g/L, 1g/L, 2g/L. Medium with no product was used as a control group. Add 1 ml of E. coli bacterial solution at a concentration of 105 cfu/ml to each petri dish, pour in about 20 ml of medium (about 45°C) and mix well. Cool and solidify and inverted culture in an incubator at 37°C for 24 hours.
Inhibitory effect on Vibrio parahaemolyticus by spread plate method: Vibrio parahaemolyticus medium was boiled and sterilized, cooled down to about 80°C and the product was added according to a certain ratio, and the product and the medium were mixed well to make the final concentration of the product 0.05g/l, 0.1g/l, 0.2g/l, 0.3g/l, 0.5g/l. Medium with no product was used as the control group. . 1ml of cultured Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacterial fluid was added to each plate, and about 20ml of medium (about 45°C) was poured and mixed well. The concentration of Vibrio parahaemolyticus sap was also determined by plate counting. After cooling and solidifying, upright incubate in 37°C constant temperature incubator for 24 hours.
Inhibitory effect on Vibrio parahaemolyticus by test tube method: the minimal inhibitory concentration of PhytoAqua and the competing product was determined by the doubling dilution method, and then the minimal bactericidal concentration of the corresponding concentration was determined by streaking plate. Brain-heart leachate broth of 3% NaCl was prepared and sterilized, and each test tube was dispensed with 5 ml. The product extract was diluted to 12.8 g/L with sterile 3% NaCl brain-heart leachate broth, which was subjected to a gradient dilution so that the final concentration of the product was 0.1 g/L, 0.2 g/L, 0.4 g/L, 0.8 g/L, 1.6 g/L, 3.2 g/L, 6.4 g/L. The final concentration of Vibrio parahaemolyticus was determined by multiplicative dilution. Add 100ul of Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacterial suspension, shake well and incubate at 37°C for 24 hours in a constant temperature incubator. The minimal product concentration that clearly inhibited bacterial growth (not turned turbid) was its minimal inhibitory concentration. The minimal bactericidal concentration is the one at which no colonies grow after the plate is streaked.
The concentration of PhytoAqua from left to right is 0 g/l, 0.1 g/L, 0.2 g/L, 0.5 g/L, 1 g/L, 2 g/L. The top and bottom are parallel controls.

The concentration of the competing product from left to right is 0 g/l, 0.1 g/L, 0.2 g/L, 0.5 g/L, 1 g/L, 2 g/L. The top and bottom are parallel control.
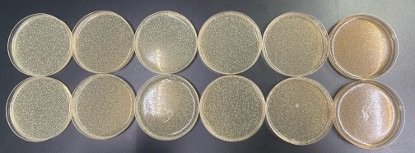
The concentration of PhytoAqua at 2 g/L can completely kill E. coli, and the competing product did not show any bacteriostatic effect at 2 g/L. It proved that the inhibitory effect of PhytoAqua on E. coli was better than that of the competing product.
The concentration of PhytoAqua from left to right is 0.05 g/l, 0.1 g/l, 0.2 g/l, 0.3 g/l, 0.5 g/l. The top and bottom are parallel controls.
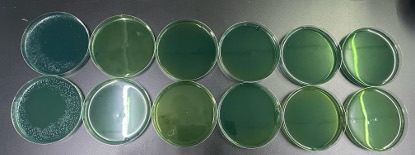
The concentrations of the competing product from left to right is 0.05 g/l, 0.1 g/l, 0.2 g/l, 0.3 g/l, 0.5 g/l. The top and bottom are parallel controls.
The concentration of PhytoAqua at 0.05 g/l and 0.1 g/l showed certain bacteriostatic effect, and the concentration of PhytoAqua at 0.2 g/l almost completely inhibited the growth of bacteria.
The concentration of the competing product at 0.05 g/l and 0.1 g/l showed certain bacteriostatic effect, but the effect was not as obvious as PhytoAqua at the concentration of 0.05 g/l, and the concentration of the competing product at 0.2 g/l had almost complete bacteriostatic effect.
The concentration of the bacterial suspension measured by plate count method was 8*106cfu/ml.
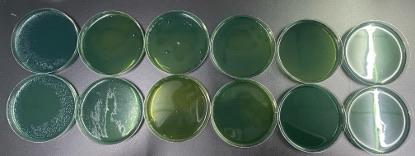
The concentration of PhytoAqua from left to right is 0.1 g/L, 0.2 g/L, 0.4 g/L, 0.8 g/L, 1.6 g/L, 3.2 g/L, 6.4 g/L.

When the concentration of PhytoAqua was 1.6 g/L, the test tube was clear. The 3.2 g/L and 6.4 g/L tubes were slightly cloudy because of the color of the emulsion itself.
The 0.8 g/L, 1.6 g/L, and 3.2 g/L test tubes were taken for streaking plate.
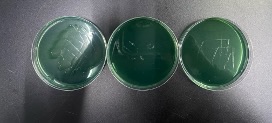
There was Vibrio growth at 0.8 g/L. There was no at 1.6 g/L and 3.2 g/L, indicating that the Minimum Bacteriostatic Concentration of PhytoAqua is from 0.8 to 1.6 g/L and the minimum bactericidal concentration is 1.6 g/L.
The concentration of the samples from left to right is 0.1 g/L, 0.2 g/L, 0.4 g/L, 0.8 g/L, 1.6 g/L, 3.2 g/L, 6.4 g/L.

The test tube was clear at a product concentration of 3.2g/L. The 0.8g/L, 1.6g/L, and 3.2g/L test tubes were taken for streaking plate.
The samples had Vibrio growth at 0.8 g/L, 1.6 g/L and had no Vibrio growth at 3.2 g/L, indicating that the Minimum Bacteriostatic Concentration of the competing product is 1.6 to 3.2g/L and the minimum bactericidal concentration is 3.2 g/L.
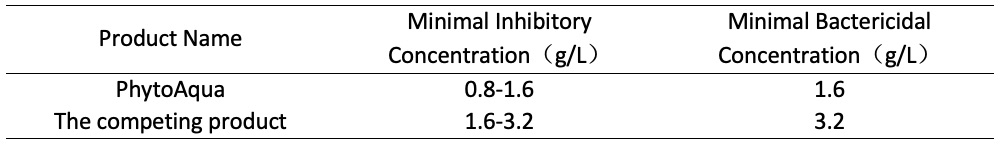
In terms of the minimal inhibitory concentration and the minimal bactericidal concentration, PhytoAqua inhibited Vibrio parahaemolyticus better than the competing product.
In this experiment, the inhibitory effect of PhytoAqua and the competing product on Vibrio parahaemolyticus was determined by the spread plate method, and it was found that 0.05 g/L PhytoAqua showed better inhibitory effect than the competing product in the spread plate method.
The test tube method and the streak plate method proved that the minimal inhibitory concentration and the minimal bactericidal concentration of PhytoAqua were lower than those of the competing product, which indicated that its inhibitory effect against Vibrio parahaemolyticus was more powerful.
The inhibitory effect of PhytoAqua and the competing product on E. coli was determined by spread plate method, and the bactericidal ability of PhytoAqua at 2 g/L was significantly higher than that of the competing product. These experiments demonstrated that PhytoAqua showed a stronger bactericidal effect than the competing product against both Vibrio parahaemolyticus and E. coli.
Ruby Yu, Head of R&D
PhytoAqua©, highly concentrated oral emulsion, based on phytogenics and medium chain fatty acids, to be added to feeds, ponds or water tanks.

Certain health statements may not be applicable in your region.