IN OTHER LANGUAGES
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a Gram-negative bacterium that can be found in coastal areas and estuaries. Rising ocean temperatures during recent years have contributed to its global dissemination.
Vibrio parahaemolyticus can infect fish, shrimp, shellfish and other aquaculture animals, especially shrimps. In shrimps, it causes acute hepatopancreas necrosis disease (AHPND), a disease previously called Early mortality syndrome (EMS). AHPND can cause up to 100% mortality within 20-30 days. It is an emerging disease that has severely damaged the global shrimp industry.
On the other hand, people who eat raw or undercooked seafood contaminated with Vibrio parahaemolyticus may experience digestive symptoms such as diarrhea, which can even lead to shock and death in severe cases. In the recent years, Vibrio parahaemolyticus contaminated seafood has become the main cause of acute gastroenteritis in the world.
Some phytogenics have antibacterial activity and have the potential to replace antibiotic growth promoters. They are widely used in the poultry and livestock industry.
In this experiment, several products which are rich in plant extracts are tested to prove their antibacterial effect against Vibrio parahaemolyticus, which lays the basis for their application in aquaculture.
The products include the oral emulsion PhytoAqua©, and the powder premixes GrowthPlus© and AroMar©.
The freeze-stored strains were inoculated into 250ml brain-heart extract broth containing 3% sodium chloride and cultured at 35℃ for 24 hours on aerobic conditions.
Oral emulsion – PhytoAqua
The test product PhtoAqua was diluted with sterilized Vibrio parahaemolyticus AGAR. The concentration of PhytoAqua in each group of media was as follows:

Pour the liquid agar into the plates, add 1 ml of the Vibrio parahaemolyticus suspension, containing 5*104 CFU. mix evenly with the medium, and cool it to room temperature for solidification
Culture at 35℃ for 24 hours.
Premix powders – GrowthPlus and Aromar
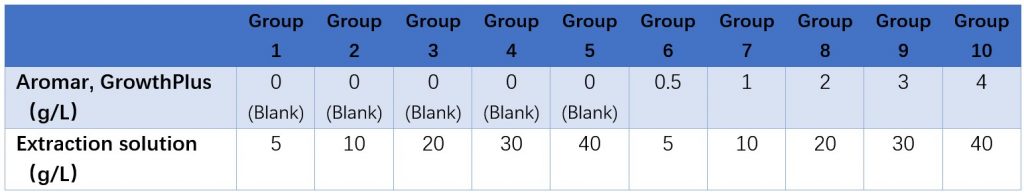
Since powder products are insoluble in water, in order to make antibacterial tests, we need to extract the raw ingredients that have anti-bacterial and anti-fungal properties into water-soluble solutions. The ratio of extraction solution and product is 10:1.
The extractions of GrowthPlus and Aromar were diluted with sterilized Vibrio parahaemolyticus agar. In order to exclude the influence of extraction reagents, different concentrations of extraction reagents were used as blank. The final concentration of components in each group of medium was as follows:
Pour the liquid agar into the plates, add 1 ml of the Vibrio parahaemolyticus suspension. containing 3.7*105 CFU. mix evenly with the medium, and cool it to room temperature for solidification
Culture at 35℃ for 24 hours.
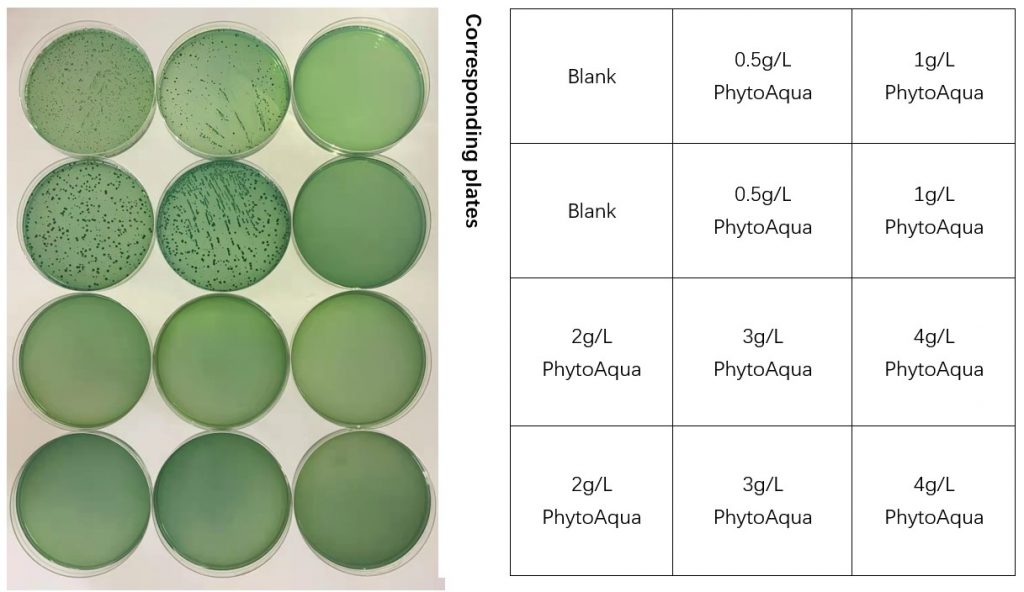
According to the culture results, 0.5 g/L PhytoAqua slightly inhibited the growth of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and groups with 1 g/L PhytoAqua or more completely inhibited its growth.
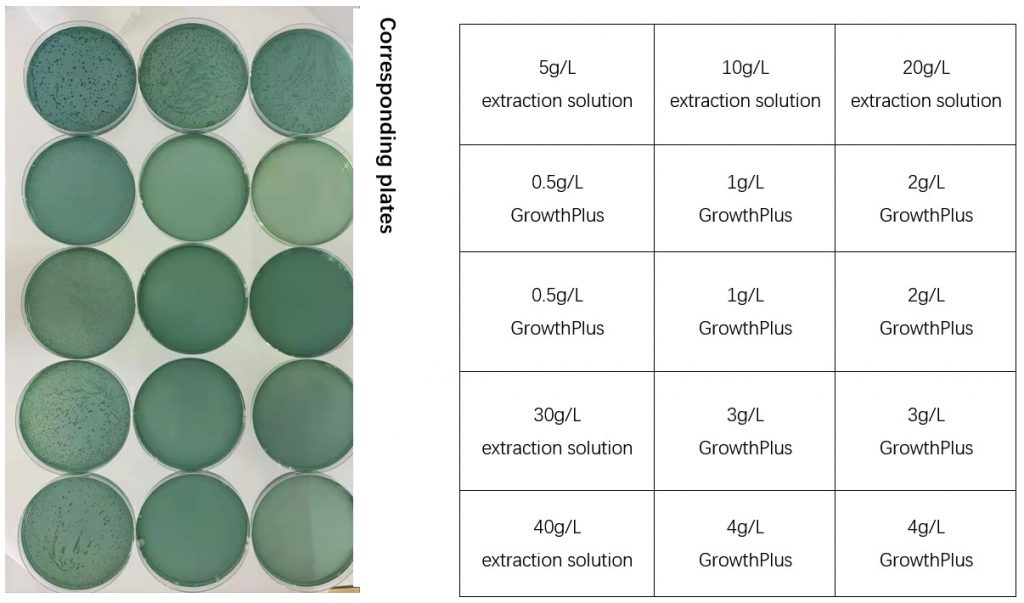
According to the culture results, 0.5 g/L GrowthPlus significantly inhibited the growth of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and groups with 1 g/L GrowthPlus or more completely inhibited its growth.
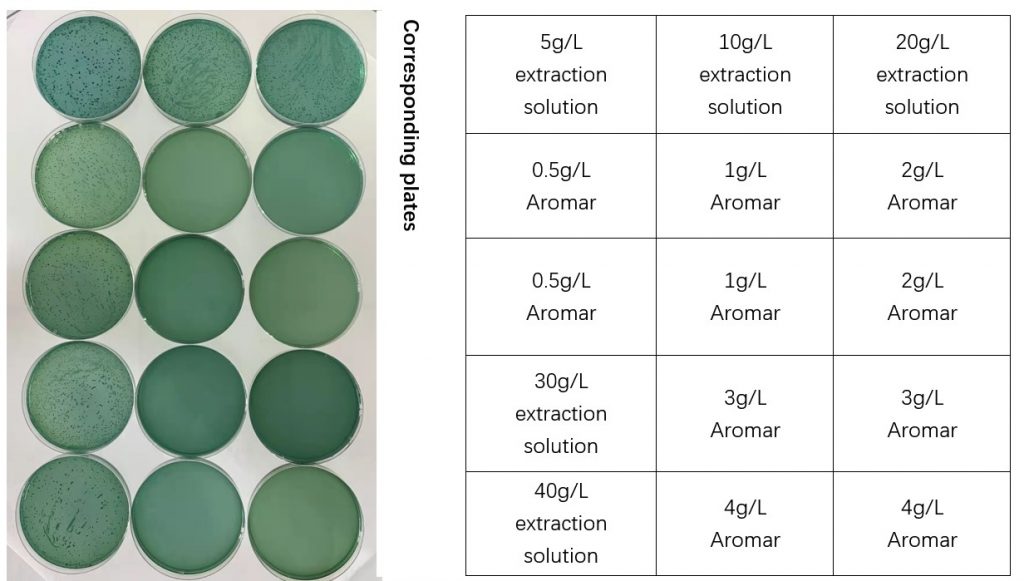
According to the culture results, 0.5 g/L AroMar slightly inhibited the growth of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and groups with 1 g/L AroMar or more completely inhibited its growth.
It is concluded that products rich in phytogenics such as PhyoAqua, Aromar, and GrowthPlus can effectively inhibit the growth of Vibrio parahaemolyticus.
This in vitro experiment supports the use of our products as part of the prevention and control strategy against Vibrio parahaemolyticus in aquaculture farms.
Ms. Ruby Yu, Research & Development
Picture found here.
AroMar©, highly concentrated premix powder that contains phytogenics and organic acids, to be added to aquaculture feeds.
PhytoAqua©, highly concentrated oral emulsion, based on phytogenics and medium chain fatty acids, to be added to feeds, ponds or water tanks.
GrowthPlus© is added to feed to maintain and improve digestive health. It is formulated with synergistic ingredients:

Certain health statements may not be applicable in your region.