16 Mar Phytogenics and antibiotics have synergistic effects

As is widely recognized, phytogenics have antibacterial properties and can replace antibiotic growth promoters. However, it is less known that, when antibiotic therapy is necessary, phytogenics and antibiotics act in synergy, increasing the effectiveness of the antibiotic.
When phytogenics and antibiotics are administered together, the dose of antibiotic needed to successfully treat the infection is lowered, and the side effects of the treatment are reduced. In in vitro tests, the presence of phytogenics reduces the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antibiotics up to 75 folds (Sanhueza et al, 2017).
Phytogenics act synergistically with antibiotics by modifying or totally inhibiting the mechanisms that bacteria have developed to acquire antibiotic resistance. The synergistic action can happen in four ways:
Modification of target sites on bacterial cell
Some bacteria become resistant to antibiotics when, thanks to a mutation, the shape of the molecule to which the antibiotic needs to bind to carry out its bactericide action (target site) changes, so that the antibiotic cannot bind to the target site and loses its effect.
Some plant extracts are able to restore the ability of the antibiotic to bind with the target site, reducing antibiotic resistance.
One example is green tea (Camellia sinensis) extract: when it is given together with beta-lactam antibiotics (penicillin, cephalosporin) it is able to increase their effectiveness against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Blocking enzymatic degradation of antibiotics
Some bacteria become resistant to antibiotics by developing enzymes that can degrade or destroy them. In example, beta-lactamases are enzymes produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics.
Both green tea and Thailand money plant (Stephania suberosa) are able to inhibit beta-lactamases, restoring the effectiveness of beta-lactam antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Increase of cell membrane permeability
The cell wall is a first barrier of bacterial defense, because antibiotics must cross it to reach their target sites.
Plant extracts rich in phenols and terpenes reduce the concentration of the lipids in the bacterial cell membrane, increasing its permeability, and facilitating the entrance of antibiotics.
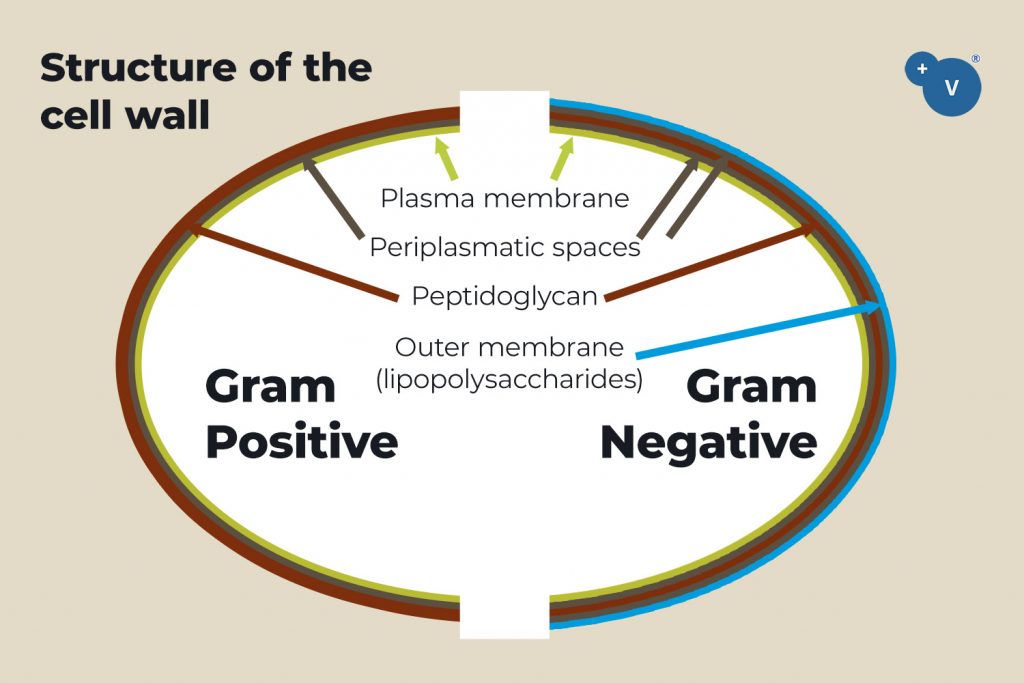
Inhibition of the efflux pumps
Efflux pumps are proteins located in the cell membrane of Gram positives and Gram negatives, that expel harmful substances from within the bacteria to the external environment.
Some bacteria develop antibiotic resistance by using efflux pumps to expel antibiotics. Many plant extracts can block efflux pumps: some examples are rosemary (Rosmarinus officinale), lemon balm (Melissa officinalis) and cassia cinnamon (Cinnamomum cassia).
The synergy between plant extracts and antibiotics has a direct application in the veterinary field. As an example, Maia et al, 2018, reported that a combination of bacupari extract (Garcinia brasiliensis) and antibiotics can increase the success of the treatment against mastitis caused by antibiotic- resistant Streptococcus spp.
We firmly believe that phytogenics have a great potential in animal health, and the results of recent investigations prove us right. Not only phytogenics can replace antibiotic growth promoters but also can help to manage infections caused by antibiotic resistant bacteria. Antibiotic resistance is one of the most serious problems of the 21st century, so this is amazing news.
Products of choice
GrowthPlus© is added to feed to maintain and improve digestive health. It is formulated with synergistic ingredients:
- Bactericidal and fungicidal plant extracts, combined with organic acids for better effectiveness, that reduce the number of pathogenic microbes in the digestive system.
- Plant extracts with prebiotic effect, that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Immunostimulant and antioxidant plant extracts.
- Silicates with mycotoxin binding function.
It is especially useful in cases of gizzard diseases, necrotic enteritis, feed passage and other enteritis. It is also used as a natural growth promoter and to replace antibiotic growth promoters.
ReproPlus© is a premix powder intended to maintain and improve digestive health in pregnant and lactating sows. It is formulated with synergistic ingredients:
- Bactericidal and fungicidal phytogenics, combined with organic acids.
- Phytogenics with immune boosting and antioxidant activity.
- Plant extracts with prebiotic effect.
- Vegetable oils rich in omega 3.
- Silicates with mycotoxin binding function.
When administered during the last period of gestation, it has a positive impact on the survivability and the health of the litter.
PigletPlus© is intended to maintain and improve digestive health. It is formulated with synergistic ingredients:
- Bactericidal and fungicidal plant extracts, combined with organic acids for better effectiveness, that reduce the number of pathogenic microbes in the digestive system.
- Plant extracts with prebiotic effect, that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Immunostimulant and antioxidant plant extracts.
- Silicates with mycotoxin binding function.
It is especially useful in cases of bacterial diarrhea during the suckling and post weaning period, and to promote growth in all ages.
AroMar©, highly concentrated premix powder that contains phytogenics and organic acids, to be added to aquaculture feeds.
Do not miss any of our articles!
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter

Certain health statements may not be applicable in your region.

