07 Jun Understanding the toxicity of mycotoxins in ducks

Although ducks are among the most sensitive species to mycotoxin contamination, the toxicity of mycotoxins in ducks is not as well studied as in chickens. On the other hand, the global production of duck meat and eggs is raising in the recent years, so it is necessary to invest more resources to investigate the harmful effects of fungal toxins in ducks, especially ducklings.
Overview
Compared to other poultry species, ducks, especially ducklings, are very sensitive to mycotoxins. They are 200 times more sensitive to aflatoxins and 10 times more sensitive to T2-toxin than broilers. Co-occurrence (contamination by more than one mycotoxin) is especially dangerous.
While in chicken it is common to find lesions by mycotoxins in gizzard and intestines, in ducks such injuries are rare. The immune system, liver and heart are the most important target organs for mycotoxins in ducks.
Deoxynivalenol (DON, vomitoxin)
Unlike in chicken, DON does not produce lesions on the surface of the digestive system of ducks. It does not affect neither nutrient absorption nor feed use, but, when combined with aflatoxins, it produces feed refusal.
The main negative effect of DON in ducks is immune suppression, especially when found in feed together with zearalenone.
T2-toxin
Ducklings (ducks 1 to 21 days old) are really sensitive to T2 toxin:
- From 0.2 ppm of T2 toxin, ducklings show oral lesions.
- From 0.3 ppm of T2 toxin, there is a reduction in weight gain and feed intake, especially if contaminated feed is fed to the ducks during several weeks.
- Higher levels of T2 toxin reduce the size of spleen and bursa of Fabricius and depress the immune response.
Aflatoxins
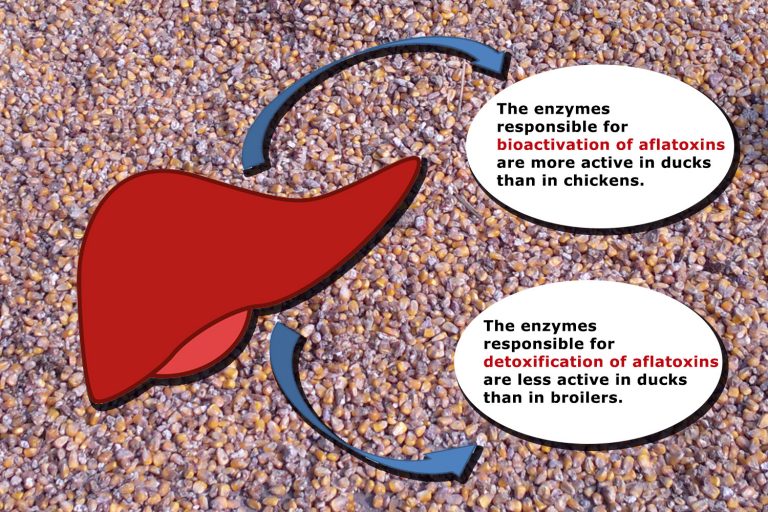
Ducklings are 200 times more sensitive to aflatoxins than broilers. The reason for this sensitivity is found in the liver: in ducks, the hepatic enzymes responsible for the bioactivation of aflatoxins are more active, while the hepatic enzymes responsible for the detoxification and elimination of aflatoxins work slower than in chicken.
Aflatoxins produce:
- Lesions in liver and bile ducts
- Alteration of blood enzymes related to liver functions
- Interference with the enzymes that digest feed in the duodenum. Decline in protein digestion and in feed energy use.
- Reduction of weight gain and worsen of FCR.
- Increase of mortality. 100% mortality at 1 ppm of total aflatoxins.
Ochratoxins
Ducks, especially ducklings, are highly susceptible to ochratoxins.
- At lower doses, ochratoxins impact the immune system and make the animals more prone to bacterial and viral diseases.
- At higher doses, ochratoxins cause severe liver toxicity.
Fumonisins
Ducks are quite resistant to the toxic effects of fumonisins, except when there is co-occurrence of fumonisins and DON in the same feed. In this case, even if both mycotoxins are found at low levels, there will be an increase of mortality in the flock.
Conclusion
It is necessary to understand the consequences of intoxication by mycotoxins in order to protect the health of ducks and to take corrective measures, such as performing the right quality control on the raw materials and adding a mycotoxin binder to duck feeds.
Products of choice
PlusBind© is a mixture of carefully selected silicates intended for the prevention of diseases and productivity losses related to the presence of all types of mycotoxins. It is indicated in poultry, pigs, aquaculture and ruminants.
The silicates present in PlusBind© have a highly expandable molecular structure. This characteristic gives the product a wide surface available for the adsorption of mycotoxins and therefore allows a high effectiveness at lower doses (0.5-1 kg per ton of feed).
PlusBind Bio© is a mixture of carefully selected silicates intended for the prevention of diseases and productivity losses related to the presence of all types of mycotoxins. It also contains plant extracts with prebiotic effect.
It is indicated in poultry, pigs and aquaculture.
The silicates present in PlusBind Bio© have a highly expandable molecular structure. This characteristic gives the product a wide surface available for the adsorption of mycotoxins and therefore allows a high effectiveness at lower doses (0.5-1 kg per ton of feed).

Certain health statements may not be applicable in your region.

